Introduction
VPS hosting, also known as Virtual Private Server hosting, is a popular choice for individuals and businesses looking for a reliable and flexible hosting solution. It combines the affordability of shared hosting with the control and performance of a dedicated server. With VPS hosting, your website is hosted on a virtual server that is partitioned, or “cut out”, from a physical server. Each virtual server runs autonomously, using its own resources and operating system.
- Introduction
- Comparing VPS to Other Web Hosting Types
- Virtual Private Server Pros and Cons
- When to Use and How to Decide If It's Time to Upgrade
- Some VPS Success Stories
- Are there VPS Alternatives? What is a Managed VPS?
- Key Features and Components of a VPS
- Additional Uses of VPS Hosting
- Choosing the Right VPS Hosting Provider
- FAQ
VPS hosting definition
This refers to the practice of hosting websites on virtual servers that are created through virtualization technology. These virtual servers mimic the functionality of dedicated servers but are more cost-effective and scalable. With VPS hosting, users have greater control over their hosting environment and can customize it to meet their specific requirements.
How does VPS hosting work?
VPS hosting works by utilizing virtualization technology to create multiple virtual servers on a single physical server. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Server virtualization: The physical server is divided into multiple virtual compartments, each functioning as an independent server. These compartments are known as virtual private servers (VPS), offering enhanced flexibility and security for various online applications and businesses.
- Resource allocation: Each virtual server is allocated a portion of the physical server’s resources, such as CPU, RAM, and storage space. This allocation ensures that the resources are dedicated to the specific compartment, or virtual server, and not shared with other compartments.
- Operating system installation: Each virtual server can have its own operating system, independent of the other virtual servers on the same physical server. This allows users to choose an operating system that suits their needs, such as Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian, as well as Windows Server.
- Isolation and security: The virtualization technology ensures that each virtual server is isolated from the others, providing enhanced security and preventing one virtual server from affecting the performance or stability of others.
- Scalability: It offers scalability, allowing users to easily upgrade or downgrade the amount of required resources on an as-needed basis. This flexibility makes it an ideal solution for websites or applications that experience fluctuating traffic or resource demands.
By leveraging virtualization technology, VPS hosting provides an affordable and reliable hosting solution that offers greater control and performance compared to shared hosting.
Comparing VPS to Other Web Hosting Types
When choosing a web hosting solution, it’s essential to understand the different types available and how they compare to VPS hosting. In this section, we will explore VPS hosting in comparison to other popular hosting options, including shared hosting, cloud hosting, WordPress hosting, and dedicated hosting.
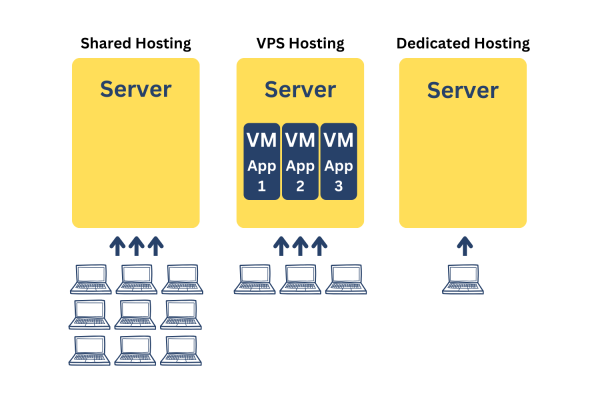
Shared Hosting
Shared hosting is a popular and cost-effective hosting option, where multiple websites are hosted on a single server. Here’s how it compares to VPS hosting:
- Resource sharing: In shared hosting, resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage are shared among multiple websites. This can lead to potential performance issues if one website experiences high traffic or is excessively hogging shared resources.
- Limited control: With shared hosting, users have limited control over server configurations and software installations since the server’s management is handled by the hosting provider.
- Suitable for small websites: Shared hosting is suitable for small websites with low to moderate traffic and minimal resource requirements.
Cloud Hosting
To host websites, cloud hosting uses a network of virtual servers. Some comparisons are:
- Scalability: Cloud hosting stands out for its exceptional scalability, empowering users with the ability to effortlessly adjust their resources, whether it be scaling up to accommodate surges in demand or scaling down during quieter periods. This inherent flexibility renders it particularly well-suited for websites characterized by ever-changing traffic patterns and varying resource requirements.
- Redundancy and reliability: Cloud hosting offers high reliability by hosting websites across multiple servers. In the event of a server failure, the website seamlessly transitions to another server, ensuring minimal downtime.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: Cloud hosting often follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where users only pay for the resources they actually use.
WordPress Hosting
WordPress hosting is designed with the purpose of supporting websites made with the WordPress platform. Some comparisons are:
- WordPress-specific optimizations: WordPress hosting typically includes optimizations for WordPress websites, such as pre-installed WordPress software, automatic updates, and specialized support.
- Simplified management: WordPress hosting providers often offer user-friendly interfaces and tools to manage WordPress websites easily.
- Limited scalability: WordPress hosting plans may have limitations on resource scalability and may not be suitable for high-traffic or resource-intensive websites.
Dedicated Hosting
Dedicated hosting provides users with an entire physical server dedicated solely to their website. Some comparisons are:
- Complete control: With dedicated hosting, users have full control over server configurations, software installations, and resource allocation.
- High performance: Dedicated hosting offers excellent performance since all server resources are dedicated to a single website.
- Higher cost: Dedicated hosting tends to be more expensive than VPS hosting as users bear the cost of an entire physical server.
In conclusion, VPS hosting strikes a balance between affordability and performance, offering greater control and resources compared to shared hosting, while being more cost-effective than dedicated hosting. Cloud hosting and WordPress hosting cater to specific needs, with cloud hosting providing scalability and redundancy, and WordPress hosting offering optimizations for WordPress websites.
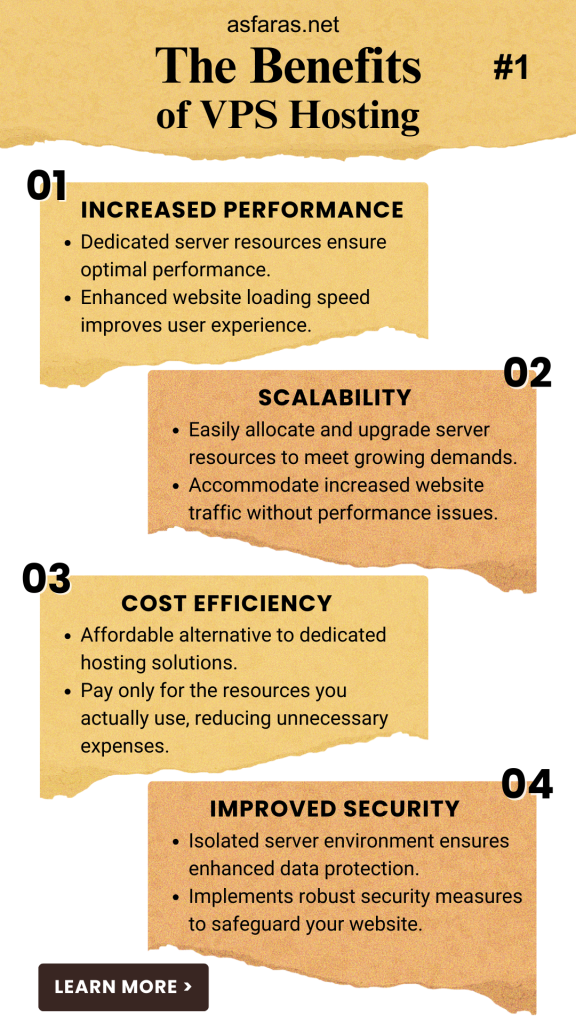
Virtual Private Server Pros and Cons
Pros
- Customization: Users can customize their server environment, including the choice of operating system, software installations, and server configurations. This level of customization provides flexibility to meet specific website requirements. For example, you can change an operating system if you are unsatisfied with it or experimenting.
- Control: With this hosting type, users have greater control over their hosting environment. They can manage server settings, install applications, and have root access to the server. This control empowers website owners to optimize performance and security according to their needs.
- Cheaper than dedicated hosting: It is a cost-effective alternative to dedicated hosting. While dedicated hosting provides an entire physical server, this type of hosting offers virtual server partitions at a fraction of the cost. This affordability makes VPS hosting a popular choice for businesses and individuals with budget constraints.
- Dedicated resources: Resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage are dedicated to the virtual server. Unlike shared hosting, where resources are shared among multiple websites, it ensures that the allocated resources are solely available for the user’s website. This dedicated resource allocation enhances performance and stability.
- Scalability: It offers scalability, allowing users to quickly scale up or down their resources as their website needs evolve. Whether it’s handling increased traffic or accommodating resource-intensive applications, it provides the flexibility to scale without disruptions. For example, you can
Cons
- Technical knowledge: Managing a VPS hosting environment requires technical knowledge and expertise. Users should be comfortable with server management, troubleshooting, and security configurations. For individuals without the necessary technical skills, managed VPS hosting services are available as an alternative.
- Higher cost than shared hosting: While it is more affordable than dedicated hosting, it generally comes at a higher cost compared to shared hosting. The dedicated resources and additional control provided by this type of hosting contribute to its higher price point.
- Responsibility for server maintenance: Users are responsible for server maintenance tasks such as software updates, security patches, and backups. This added responsibility requires time and effort to ensure the server remains secure and up-to-date.
- Limited physical resources: Despite the dedicated resource allocation of VPS hosting, the virtual server still operates within the limitations of the physical server it is hosted on. If the physical server experiences hardware issues or resource saturation, it can impact the performance of the virtual servers.
When to Use and How to Decide If It’s Time to Upgrade
If you’re currently using a different hosting solution and considering upgrading to VPS hosting, it’s essential to evaluate the signs indicating the need for an upgrade and consider relevant factors before making a decision. Let’s explore when to use this hosting type and how to decide if it’s time to upgrade.

Signs that you may need to upgrade
- Increased website traffic: If your website experiences a significant increase in traffic, shared hosting may struggle to handle the load. Slow loading times, performance issues, and frequent downtime can be signs that it’s time to upgrade to VPS hosting, which provides dedicated resources to handle higher traffic volumes.
- Resource limitations: If your website’s resource requirements exceed what shared hosting can provide, such as the need for more CPU power, RAM, or storage space, it’s a sign that upgrading to VPS hosting is worth considering. VPS hosting offers scalability and flexibility to meet growing resource demands.
- Security concerns: If you require enhanced security measures for your website, VPS hosting can offer additional protection. Shared hosting environments are more susceptible to security breaches as multiple websites share the same server. Upgrading to VPS hosting provides isolation and stronger security measures.
- Custom software or configurations: If your website requires specific software installations, for example, Google Analytics or a Customer Relationship Management system, custom server configurations, or root access, shared hosting may not offer the necessary flexibility. VPS hosting grants you greater control and customization options, making it suitable for websites with unique requirements.
Factors to consider when deciding to upgrade
When deciding whether to upgrade to VPS hosting, consider the following factors:
- Website needs: Evaluate your website’s current and future needs. Consider factors such as expected traffic growth, resource requirements, and the need for customization. If your website’s demands align with the benefits offered by this type of hosting, an upgrade may be warranted.
- Budget: Assess your budget and determine if you can allocate funds to a VPS hosting plan. While it is more affordable than dedicated hosting, it is typically pricier than shared hosting. Ensure that the cost of upgrading fits within your budget constraints.
- Technical expertise: Consider your technical knowledge and ability to manage a VPS hosting environment. If you have the necessary skills or are willing to invest time in learning server management, VPS hosting can be a viable option. Alternatively, managed VPS hosting services are available for users who prefer professional assistance.
- Future scalability: Anticipate your website’s growth and scalability requirements. VPS hosting offers scalability options, allowing you to easily upgrade resources as your website expands. If future scalability is a priority, upgrading can provide the necessary flexibility.
By assessing signs like increased traffic, resource limitations, security concerns, and the need for customization, along with considering factors like website needs, budget, technical expertise, and future scalability, you can make an informed decision about upgrading to VPS hosting.

Some VPS Success Stories
Emirates Flies High After Massive AWS Migration
- Emirates successfully migrated to AWS, cutting costs and improving services during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Over 30 business-critical applications were moved to AWS from colocation centers.
- The migration allowed rapid scaling based on demand and enhanced transparency.
- Significant cost savings are expected, and the migration had zero unplanned downtime.
How Jiji is Building a Trusted Classifieds Marketplace
- Jiji, a leading African online classifieds marketplace, uses DigitalOcean services for its e-commerce platform.
- Founded in Lagos, Nigeria, in 2014, Jiji connects buyers and sellers across Africa, providing a secure and user-friendly platform.
- They chose DigitalOcean for its affordability and functionality.
- Premium CPU-Optimized Droplets (i.e. VPS) improved server response times.
How Jhon Scaled His Minecraft Business With Hostinger
- Jhon Ortega’s journey from Minecraft enthusiast to successful online entrepreneur with Netherix Studios, supported by Hostinger.
- Initial struggles with website building led him to Hostinger’s user-friendly Premium Shared Hosting.
- Facing resource challenges, Jhon upgraded to VPS 2 hosting, significantly boosting his business revenue.
- Later, he transitioned to Cloud Hosting, benefiting from its performance and ease of use.
- Jhon’s success mirrors Hostinger’s mission of empowering users and highlights the importance of professional websites.
- Future plans include exploring the official Minecraft marketplace and collaborating with a popular game YouTuber.
Are there VPS Alternatives? What is a Managed VPS?
When considering VPS hosting, it’s essential to be aware of alternative options and understand the concept of managed VPS hosting. We’ll now explore these alternatives and explain what managed VPS hosting entails.
Managed VPS hosting
This is a type of hosting where the hosting provider takes care of the server management tasks on behalf of the user. Here’s what you need to know:
- Server management: The hosting provider handles server management tasks such as software installations, security updates, server monitoring, and backups. This frees up the user from the technical aspects of server administration, allowing them to focus on their website.
- Technical support: It typically includes comprehensive technical support. The hosting provider’s support team is available to assist with any server-related issues or inquiries. This support can be valuable for users who lack technical expertise or prefer to rely on professional assistance.
- Convenience and peace of mind: It offers convenience and peace of mind by offloading server management responsibilities. Users can rely on the expertise of the hosting provider, ensuring that their server is properly maintained, secure, and optimized for performance.
Unmanaged VPS hosting
Unmanaged VPS hosting, on the other hand, requires users to have more technical knowledge and take full responsibility for server management. Here are the key points to understand:
- Complete control: Users have full control over their server environment. They are responsible for configuring the server, installing software, managing security measures, and performing regular maintenance tasks.
- Technical expertise required: It is suitable for users with technical proficiency in server administration. They should be comfortable with tasks such as server setup, software configurations, troubleshooting, and security management.
- Greater flexibility: It offers greater flexibility in terms of customization and software choices. Users have the freedom to configure the server according to their specific needs and preferences.
Semi-managed VPS hosting
Semi-managed VPS hosting is a middle ground between managed and unmanaged hosting. Here’s what you should know:
- Partial server management: In semi-managed VPS hosting, the hosting provider handles certain server management tasks, while the user is responsible for others. The specific division of responsibilities may vary depending on the hosting provider.
- Common tasks handled by the provider: The hosting provider typically takes care of essential server maintenance tasks such as hardware maintenance, network monitoring, and infrastructure updates. The user retains control over their website-specific configurations and software installations.
- Customizable support: Semi-managed VPS hosting often provides customizable support options. Users can choose the level of assistance they require from the hosting provider, whether it’s for troubleshooting, software installations, or performance optimizations.
Key Features and Components of a VPS
Understanding the key features and components of a Virtual Private Server (VPS) is essential when considering this hosting solution. In this section, we will delve into the important aspects of a VPS.

Virtualization technology
Virtualization technology lies at the core of a VPS and enables the creation of multiple virtual servers on a single physical server. Here’s what you should know about virtualization technology in a VPS:
- Hypervisor: The hypervisor is the software layer that manages the virtualization process. It allows the physical server to be divided into multiple virtual compartments, each functioning as an independent server.
- Isolation: Virtualization provides a high level of isolation between the virtual servers. Each VPS operates independently, with its own allocated resources and dedicated environment. This isolation ensures that one VPS cannot impact the performance or security of another.
- Resource allocation: Virtualization technology enables the allocation of specific resources to each VPS, including CPU power, RAM, storage space, and bandwidth. These resources are dedicated to the respective VPS and are not shared with other virtual servers.
Hardware specifications
The hardware specifications of the physical server hosting the VPS play a crucial role in determining the performance and capabilities of the virtual servers. Here are the main components to think about:
- CPU: The central processing unit (CPU) is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. The CPU’s processing power affects the speed and efficiency of the VPS.
- RAM: Random Access Memory (RAM) is the temporary storage used by the VPS to store data that is actively being processed. Sufficient RAM ensures smooth performance and the ability to handle multiple simultaneous tasks.
- Storage: VPS hosting typically offers various storage options, including traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) and faster solid-state drives (SSDs). Storage capacity and speed directly impact the performance and storage capabilities of the VPS.
- Network connectivity: The physical server should have reliable and high-speed network connectivity to ensure fast and uninterrupted data transfer between the VPS and the internet.
Operating system options
VPS hosting allows users to choose their preferred operating system (OS) for the virtual server. Here are the key points regarding operating system options:
- Windows: VPS hosting supports Windows-based operating systems, such as Windows Server, which are suitable for websites and applications developed using Microsoft technologies.
- Linux: Linux-based operating systems, such as Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian, are commonly used in VPS hosting. Linux offers a wide range of distributions and is known for its stability, security, and flexibility.
- Other options: Depending on the hosting provider, additional operating system options may be available, such as FreeBSD or custom OS images.
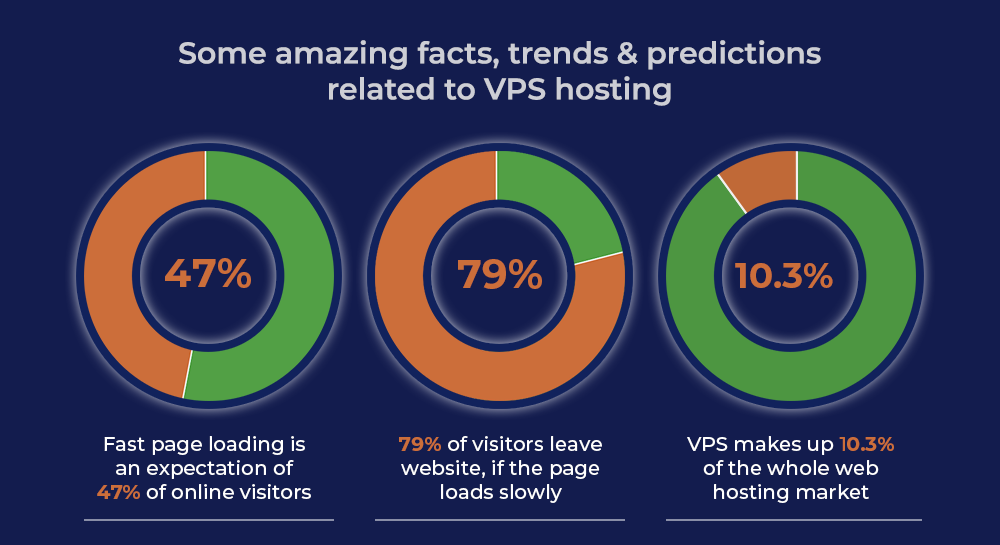
Website conversion rates drop by 4.42% with each second of load time that goes by between zero and five seconds. Website speed really matters for user experience and your profits. Many studies, including our research at Portent, show that it affects how many people buy from your site. A look at data from 20 websites and over 27,000 pages, checking out more than 100 million views. For B2B websites, here’s what was found:
– 82% of pages load in 5 seconds or less.
– A site that loads in 1 second has 3 times more sales than a 5-second site.
– A site loading in 1 second has 5 times more sales than one taking 10 seconds.
Additional Uses of VPS Hosting
VPS hosting offers a wide range of applications and benefits that make it a popular choice for many users. We will explore some more common uses.

Building test environments
VPS hosting is often used to create test environments for development and quality assurance purposes. Here’s how VPS hosting facilitates the building of test environments:
- Isolation: Each VPS instance operates independently, providing a controlled and isolated environment for testing. Developers can test their applications without affecting the production environment or other testing environments.
- Flexibility: VPS hosting offers flexibility in configuring test environments. Developers can replicate the production environment or create custom setups to simulate different scenarios and test various aspects of their applications.
- Snapshot and rollback: VPS hosting allows users to take snapshots of their VPS instances at different stages of testing. If an issue occurs, they can roll back to a previous snapshot, ensuring a stable state for further testing.
Secondary storage
VPS hosting can serve as secondary storage for various purposes. Here are some common applications of this type of hosting for secondary storage:
- Backup and disaster recovery: A VPS can be used to store backups of important data and files. Users can set up automated backup processes and securely store their data on the VPS, ensuring redundancy and the ability to recover in case of data loss.
- File storage and sharing: A VPS can be used as a file storage and sharing solution. Users can upload files to their VPS and share them with others, either privately or publicly, making it a convenient alternative to traditional file hosting services.
- Archiving: A VPS can be utilized for long-term archiving of data and files that are not frequently accessed. Users can store historical records, documents, or media files on the VPS, freeing up space on their local devices.
In summary, a VPS can be used for more than just hosting websites. It is also popular for building test environments, offering isolation, flexibility, and snapshot capabilities. Additionally, it can serve as secondary storage for backup and disaster recovery, file storage and sharing, and archiving purposes.
Choosing the Right VPS Hosting Provider
Choosing the right VPS hosting provider is crucial to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and support for your virtual server. In this section, we will discuss the factors to consider when selecting a provider, key features to look for, and how to evaluate reliability and support.
Factors to consider when selecting a provider
When choosing a VPS hosting provider, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Performance: Look for a provider that offers high-performance hardware and network infrastructure to ensure fast and responsive VPS hosting.
- Scalability: Consider the provider’s ability to accommodate your growing needs. Ensure they offer flexible upgrade options to increase resources as your requirements expand.
- Security: Assess the provider’s security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular backups, to safeguard your VPS and data from potential threats.
- Cost: Compare the pricing plans offered by different providers. Consider the balance between cost and the features and resources provided.
Key features to look for
When evaluating VPS hosting providers, pay attention to the following key features:
- Management interface: Look for a provider that offers a user-friendly management interface, such as a control panel, to simplify server administration tasks.
- Operating system options: Ensure the provider offers a variety of operating system choices, including both Windows and Linux distributions, to suit your specific needs.
- Resource allocation: Check if the provider allows flexible resource allocation, enabling you to adjust CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth according to your requirements.
- Backup and restore options: Consider if the provider offers automated backup and restore capabilities, ensuring the safety of your data and the ability to recover in case of unexpected incidents.
Evaluating reliability and support
To assess the reliability and support provided by a VPS hosting provider, consider the following factors:
- Uptime guarantee: Look for a provider that offers a high uptime guarantee, indicating the amount of time their network and servers are expected to be operational.
- Customer reviews: Read reviews and testimonials from existing customers to gauge their satisfaction with the provider’s reliability and customer support.
- Technical support: Evaluate the provider’s technical support options, such as 24/7 availability, multiple communication channels, and knowledgeable support staff, to ensure prompt assistance when needed.
- Service level agreement (SLA): Review the provider’s SLA, which outlines the terms and conditions of their service, including response times, compensation policies, and service availability guarantees.
In a nutshell, when you’re in the process of choosing a VPS hosting provider, it’s crucial to consider several key factors: performance, scalability, security, and cost. Also, be sure to keep an eye out for important features like an easy-to-use management interface, a wide variety of operating system options, the flexibility to allocate resources as needed, and robust backup and restoration capabilities. Plus, it’s a good idea to assess reliability and support, which includes checking out uptime guarantees, reading customer reviews, exploring technical support options, and reviewing service level agreements (SLAs).
Case Studies and Examples of Businesses Benefiting from VPS Hosting
VPS hosting has proven to be a valuable solution for businesses across various industries. In this section, we will explore real-world examples of successful VPS implementations and discuss the industries and use cases where VPS hosting has provided significant benefits.

Real-world examples of successful VPS implementations
Here are a few examples of businesses that have benefited from using VPS hosting:
- E-commerce websites: Many e-commerce businesses rely on VPS hosting to ensure fast and secure online shopping experiences for their customers. VPS allows them to handle high-traffic volumes, manage inventory, process transactions, and maintain customer databases effectively.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) providers: SaaS companies often utilize VPS hosting to deliver their software applications to customers. VPS enables them to scale resources based on customer demands, ensure data security and privacy, and provide reliable access to their software platforms.
- Media and content distribution: Media companies that deliver high-quality video, audio, or other digital content often leverage VPS hosting to handle the storage and distribution of their media files. VPS allows them to deliver content efficiently to a global audience while maintaining fast loading speeds.
- Development and testing environments: VPS hosting is popular among software development teams for creating isolated development and testing environments. Developers can deploy multiple VPS instances to simulate different environments, test software compatibility, and ensure smooth deployment to production servers.
Industries and use cases for VPS hosting
VPS hosting finds applications across various industries and use cases. Here are a few examples:
- Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs): VPS hosting is an ideal solution for SMBs that require a cost-effective hosting environment with flexibility and scalability. It enables them to establish an online presence, host websites, run applications, and manage data without the need to invest in expensive dedicated servers.
- Web hosting providers: Web hosting companies often utilize VPS hosting to offer hosting services to their clients. VPS allows them to create virtualized hosting environments for multiple customers while providing each customer with dedicated resources and control over their hosting environment.
- Data analytics and big data processing: VPS hosting can support data analytics and big data processing tasks that require significant computing power and resources. It allows businesses to process and analyze large volumes of data efficiently, enabling insights and informed decision-making.
- Remote desktop and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI): VPS hosting can power remote desktop and VDI solutions, enabling users to access their desktop environments and applications from anywhere, using any device. This is particularly valuable for remote work scenarios and businesses that require centralized management of desktop environments.
To summarize, VPS hosting has demonstrated its advantages in a wide range of industries and applications. Concrete instances include e-commerce websites, SaaS providers, media and content distribution, as well as development and testing environments. Furthermore, VPS hosting is highly beneficial for SMBs, web hosting providers, data analytics, and remote desktop/VDI solutions. By utilizing the flexibility, scalability, and resource allocation capabilities offered by VPS hosting, businesses can efficiently address their hosting and infrastructure requirements.
Future Trends and Advancements in VPS Hosting
VPS hosting continues to evolve with the advancements in technology and the changing needs of businesses. We will explore emerging technologies and innovations in VPS hosting and make predictions for the future of this hosting solution.
Emerging technologies and innovations in VPS hosting
Here are some emerging technologies and innovations that are shaping the future of VPS hosting:
- Containerization: Containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes are gaining popularity in the hosting industry. They provide lightweight and isolated environments for applications, allowing for efficient resource allocation and scalability. VPS hosting providers are integrating containerization technologies to offer more flexible and streamlined hosting solutions.
- Serverless computing: Serverless computing models, such as AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions, are revolutionizing the way applications are deployed and run. In a serverless architecture, businesses no longer need to provision and manage servers. VPS hosting providers are exploring ways to incorporate serverless computing into their offerings, providing customers with more cost-effective and scalable options.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration: The integration of AI into VPS hosting brings intelligent automation and optimization capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze resource usage patterns, predict demand, and dynamically allocate resources to maximize performance and cost-efficiency. VPS hosting providers are leveraging AI technologies to enhance resource management and deliver better experiences for their customers.
Predictions for the future of VPS
Looking ahead, here are some predictions for the future of VPS hosting:
- Increased adoption of edge computing: With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the need for low-latency applications, edge computing is gaining momentum. VPS hosting providers will likely extend their infrastructure to edge locations, enabling businesses to deploy their VPS instances closer to end-users for improved performance and reduced network latency.
- Enhanced security and privacy features: As cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, VPS hosting providers will invest in robust security measures. This includes implementing advanced encryption protocols, intrusion detection systems, and proactive monitoring to safeguard customer data and ensure privacy.
- Seamless multi-cloud integration: Businesses are increasingly adopting multi-cloud strategies to leverage the strengths of different cloud providers. VPS hosting providers will focus on developing tools and technologies that enable seamless integration and management of VPS instances across multiple cloud platforms, providing customers with greater flexibility and agility.
- Green hosting initiatives: Environmental sustainability is becoming a significant concern in the hosting industry. VPS hosting providers will likely prioritize energy-efficient infrastructure and renewable energy sources to reduce their carbon footprint. Green hosting initiatives will gain prominence, attracting businesses that prioritize environmentally friendly solutions.
The trajectory of VPS hosting is being influenced by emerging technologies like containerization, serverless computing, and AI integration. Forecasts for the future encompass wider acceptance of edge computing, improved security and privacy functionalities, seamless integration with multiple cloud platforms, and initiatives for environmentally friendly hosting. By embracing these trends and advancements, VPS hosting will persistently adapt to cater to the changing requirements of businesses in a dynamic digital environment.
FAQ
Bukeda has over 18 years of IT experience. With certifications in MCSA, MCDBA, MCSE, and MC-AzA in Microsoft Azure, he is proficient in web development, databases, server infrastructure, virtualization, and cloud computing. He has worked with USAID contractors, aviation companies and contributed to World Bank projects.



